CSS Forums
Friday, April 19, 2024
01:55 PM (GMT +5)
01:55 PM (GMT +5)
|
#21
|
||||
|
||||
|
T taiga biome The region of coniferous forest extending across much of northern Europe, Asia, and North America; characterized by long, cold winters and short, cool summers and by acidic, thin soils. tap root A primary root that grows vertically downward and gives off small lateral roots; occurs in dicots. Root system in plants characterized by one root longer than the other roots. Example: carrot. target cell A cell that a particular hormone effects by its direct action (either passing through the membrane or binding to a surface receptor).  tarsals The bones that make up the ankle joint. taxis The behavior when an animal turns and moves toward or away from an external stimulus (pl.: taxes). taxon Term applied group of organisms comprising a given taxonomic category taxonomy A systematic method of classifying plants and animals. Classification of organisms based on degrees of similarity purportedly representing evolutionary (phylogenetic) relatedness. T cells The type of lymphocyte responsible for cell-mediated immunity; also protects against infection by parasites, fungi, and protozoans and can kill cancerous cells; circulate in the blood and become associated with lymph nodes and the spleen. tectonic plates Segments of the lithosphere that comprise the surface of the Earth much the way a turtle shell is composed of its plates. telophase The Þnal stage of mitosis in which the chromosomes migrate to opposite poles, a new nuclear envelope forms, and the chromosomes uncoil. The last phase of nuclear division in eukaryotes when the segregated chromosomes uncoil and begin to reform nuclei. This is immediately followed (in most cases) by cytokinesis. temperate forest biome Extends across regions of the northern hemisphere with abundant rainfall and long growing seasons. Deciduous, broad-leaved trees are the dominant plants. template strand The strand of DNA that is transcribed to make RNA. 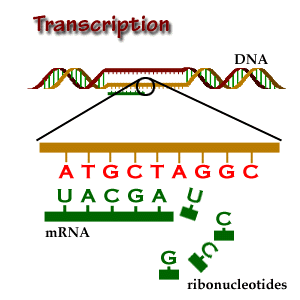 temporal lobe The lobe of the cerebral cortex that is responsible for processing auditory signals. tendons Bundles of connective tissue that link muscle to bone. Fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. .  terminal buds Buds located at the end of a plant shoot. termination The end of translation; occurs when the ribosome reaches the stop codon on the messenger RNA molecule and the polypeptide, the messenger RNA, and the transfer RNA molecule are released from the ribosome.  termination codon One of three three-base sequences that initiate termination of the protein synthesis process. tertiary structure The folding of a protein's secondary structure into a functional three-dimensional conÞguration. Shape assumed by protein due to interactions between amino acids far apart on the chain. test cross Genetic crossing of an organism with known genotype (one that exhibits the recessivephenotype) with an individual expressing the dominant phenotype but of unknown heritage. tetrad The four chromatids in each cluster during synapsis; formed by the two sister chromatids in each of the two homologous chromosomes. thalamus The brain region that serves as a switching center for sensory signals passing from the brain stem to other brain regions; part of the diencephalon. thecodonts An informal term for a variety of Permian and Triassic reptiles that had teeth set in individual sockets. Small, bipedal thecodontians are the probable ancestors of dinosaurs. theory A hypothesis that has withstood extensive testing by a variety of methods, and in which a higher degree of certainty may be placed. A theory is NEVER a fact, but instead is an attempt to explain one or more facts. thermacidophiles A group of archaebacteria that are able to tolerate high temperatures and acidic pH. thermiogenesis The generation of heat by raising the body's metabolic rate; controlled by the hypothalamus. thermoregulation The regulation of body temperature. thigmotropism Plants' response to contact with a solid object; e.g., tendrils' twining around a pole. Plant response to touch. thoracic cavity The chest cavity in which the heart and lungs are located. thorax In many arthropods, one of three regions formed by the fusion of the segments (others are the head and abdomen). thorns Stems modified to protect the plant. thoroughfare channels Shortcuts within the capillary network that allow blood to bypass a capillary bed.  thylakoids The specialized membrane structures in which photosynthesis takes place. Internal membranes in the chloroplast where the light reaction chemicals are embedded. Collections of thylakoids form the grana. thymine One of the pyrimidine bases in DNA, thymine is replaced by uracil in RNA. thyroid-stimulating hormone A hormone produced by the anterior pituitary that stimulates the production and release of thyroid hormones. tight junctions Junctions between the plasma membranes of adjacent cells in animals that form a barrier, preventing materials from passing between the cells. tissues Groups of similar cells organized to carry out one or more speciÞc functions. Groups of cells performing a function in a multicellular organism. toxins Term applied to poisons in living systems. trace fossil Any indication of prehistoric organic activity, such as tracks, trails, burrows, or nests. trachea In insects and spiders, a series of tubes that carry air directly to cells for gas exchange; in humans, the air-conducting duct that leads from the pharynx to the lungs. tracheids Long, tapered cells with pitted walls that form a system of tubes in the xylem and carry water and solutes from the roots to the rest of the plant. One type of xylem cells. Tracheids are long and relatively narrow, and transport materials from the roots upward. Tracheids are dead at maturity and have lignin in their secondary walls.  transcription The synthesis of RNA from a DNA template. The making of RNA from one strand of the DNA molecule. transfer RNAs (tRNAs) Small, single-stranded RNA molecules that bind to amino acids and deliver them to the proper codon on messenger RNA. The trucks of protein synthesis that carry the specified amino acid to the ribosome. Abbreviated tRNA.  transformation In GrifÞth's experiments with strains of pneumonia bacterium, the process by which hereditary information passed from dead cells of one strain into cells of another strain, causing them to take on the characteristic virulence of the Þrst strain. transforming factor GrifÞth's name for the unknown material leading to transformation; later found to be DNA. transition reaction Biochemical process of converting 3-carbon pyruvate into 2-carbon acetyl and attaching it to coenzyme A (CoA) so it can enter Kreb's cycle. Carbon dioxide is also released and NADH is formed (from NAD and H) in this process. translation The synthesis of protein on a template of messenger RNA; consists of three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. Making of a polypeptide sequence by translating the genetic code of an mRNA molecule associated with a ribosome.  translocation 1)The movement of a segment from one chromosome to another without altering the number of chromosomes. 2) the movement of þuids through the phloem from one part of a plant to another, with the direction of movement depending on the pressure gradients between source and sink regions.  transpiration The loss of water molecules from the leaves of a plant; creates an osmotic gradient; producing tension that pulls water upward from the roots.  Triassic Period The first period of the Mesozoic Era between 225 and 185 million years ago. Pangaea began to breakup during this time. The ancestors of dinosaurs were present, as were early mammals and mammal-like reptiles. trichomes Extensions from the epidermis of the plant that provide shade and protection for the plant. trichocysts Barbed, thread-like organelles of ciliated protozoans that can be discharged for defense or to capture prey. trilobites A group of benthonic, detritus-feeding, extinct marine invertebrate animals (phylum Arthropoda), having skeletons of an organic compound called chitin. Trilobites appear in abundance early in the Cambrian period and were dominant animals in the Burgess Shale fauna, before finally becoming extinct at the end of the Permian period.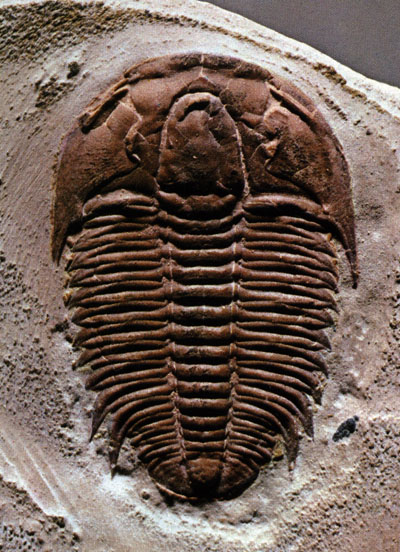  triplet Three-base sequence of mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid or termination codon. trisomy A condition where a cell has an extra chromosome. trophoblast The outer layer of cells of a blastocyst that adhere to the endometrium during implantation. tropical rain forest biome The most complex and diverse biome; found near the equator in South America and Africa; characterized by thin soils, heavy rainfall, and little þuctuation in temperature. tropic hormone Hormone made by one gland that causes another gland to secrete a hormone. tropism The movement of plant parts toward or away from a stimulus in the plant's environment. Plant movement in response to an environmental stimulus. true-breeding Occurs when self-fertilization gives rise to the same traits in all offspring, generation after generation. Now interpreted as equivalent to homozygous. trypanosomes A type of roundworm, responsible for human disease associated with eating raw or undercooked pork. tubal ligation A contraceptive procedure in women in which the oviducts are cut, preventing the ova from reaching the uterus. tubal pregnancy Occurs when the morula remains in the oviduct and does not descend into the uterus. tube-within-a-tube system A type of body plan in animals. The organism has two openings&emdash;one for food and one for the elimination of waste&emdash;and a specialized digestive system. tube nucleus One of the cells in the male gametophyte in seed plants. The tube nucleus grows through the stigma, style, and into the ovule, clearing the way for the sperm nuclei to enter the embryo sac. tubers Swollen underground stems in plants that store food, such as the irish potato. tubular secretion The process in which ions and other waste products are transported into the distal tubules of the nephron. tubulins The protein subunits from which microtubules are assembled. tumor suppressor genes Genes that normally keep cell division under control, preventing the cell from responding to internal and external commands to divide. tundra biome Extensive treeless plain across northern Europe, Asia, and North American between the taiga to the south and the permanent ice to the north. Much of the soil remains frozen in permafrost, and grasses and other vegetation support herds of large grazing mammals. turgor pressure Pressure caused by the cytoplasm pressing against the cell wall. Turner syndrome In humans, a genetically determined condition in which an individual has only one sex chromosome (an X). Affected individuals are always female and are typically short and infertile. |
|
#22
|
||||
|
||||
|
U umbilical cord The structure that connects the placenta and the embryo; contains the umbilical arteries and the umbilical vein. unicellular Single-celled. uniformitarianism The idea that geological processes have remained uniform over time and that slight changes over long periods can have large-scale consequences; proposed by James Hutton in 1795 and reŞned by Charles Lyell during the 1800s.The principle on which modern geology was founded: processes operating today on the earth operated in much the same way in the geologic past. Sometimes expressed as "the present is the key to the past". uninucleate Term applied to cells having only a single nucleus. unsaturated fat A triglyceride with double coavent bonds between some carbon atoms. uracil The pyrimidine that replaces thymine in RNA molecules and nucleotides. ureter A muscular tube that transports urine by peristaltic contractions from the kidney to the bladder. urine Fluid containing various wastes that is produced in the kidney and excreted from the bladder. uterus The organ that houses and nourishes the developing embryo and fetus. The womb. Female reproductive organ in which the fertilized egg implants.
__________________
The Me you have always known, the Me that's a stranger still. Last edited by Last Island; Friday, August 10, 2007 at 04:15 PM. |
|
#23
|
||||
|
||||
|
V vaccination The process of protecting against infectious disease by introducing into the body a vaccine that stimulates a primary immune response and the production of memory cells against the disease-causing agent. vaccine A preparation containing dead or weakened pathogens that when injected into the body elicit an immune response. vacuoles Membrane-bound şuid-Şlled spaces in plant and animal cells that remove waste products and store ingested food. vascular bundle Groups of xylem, phloem and cambium cells in stems of plants descended from the procambium embryonic tissue layer.  vascular cambium A layer of lateral meristematic tissue between the xylem and phloem in the stems of woody plants. Lateral meristem tissue in plants that produces secondary growth. vascular cylinder A central column formed by the vascular tissue of a plant root; surrounded by parenchymal ground tissue. vascular parenchyma Specialized parenchyma cells in the phloem of plants. vascular plants Group of plants having lignified conducting tissue (xylem vessels or tracheids). vascular system Specialized tissues for transporting şuids and nutrients in plants; also plays a role in supporting the plant; one of the four main tissue systems in plants. vas deferens The duct that carries sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct and urethra.The tube connecting the testes with the urethra. vectors Self-replicating DNA molecules that can be joined with DNA fragments to form recombinant DNA molecules. veins Thin-walled vessels that carry blood to the heart. Units of the circulatory system that carry blood to the heart. ventilation The mechanics of breathing in and out through the use of the diaphragm and muscles in the wall of the thoracic cavity. ventral Term applied to the lower side of a fish, or to the chest of a land vertebrate. ventricle The chamber of the heart that pumps the blood into the blood vessels that carry it away from the heart. The lower chamber of the heart through which blood leaves the heart. venules The smallest veins. Blood şows into them from the capillary beds. Small veins that connect a vein with capillaries.  vernalization ArtiŞcial exposure of seeds or seedlings to cold to enable the plant to şower. vertebrae The segments of the spinal column; separated by disks made of connective tissue (sing.: vertebra). vertebrate Any animal having a segmented vertebral column; members of the subphylum Vertebrata; include reptiles, Şshes, mammals, and birds. vesicles Small membrane-bound spaces in most plant and animal cells that transport macromolecules into and out of the cell and carry materials between organelles in the cell. vessel elements Short, wide cells arranged end to end, forming a system of tubes in the xylem that moves water and solutes from the roots to the rest of the plant. Large diameter cells of the xylem that are extremely specialized and efficient at conduction. An evolutionary advance over tracheids. Most angiosperms have vessels. vestigial structures Nonfunctional remains of organs that were functional in ancestral species and may still be functional in related species; e.g., the dewclaws of dogs. villi Finger-like projections of the lining of the small intestine that increase the surface area available for absorption. Also, projections of the chorion that extend into cavities Şlled with maternal blood and allow the exchange of nutrients between the maternal and embryonic circulations. Projections of the inner layer of the small intestine that increase the surface area for absorbtion of food. viroids Infective forms of nucleic acid without a protective coat of protein; unencapsulated single-stranded RNA molecules. Naked RNA, possibly of degenerated virus, that infects plants. virus Infectious chemical agent composed of a nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) inside a protein coat. vitamins A diverse group of organic molecules that are required for metabolic reactions and generally cannot be synthesized in the body.
__________________
The Me you have always known, the Me that's a stranger still. |
|
#24
|
||||
|
||||
|
W white blood cell Component of the blood that functions in the immune system. Also known as a leukocyte. wood The inner layer of the stems of woody plants; composed of xylem. X X-chromosome One of the sex chromosomes. xerophytic leaves The leaves of plants that grow under arid conditions with low levels of soil and water. Usually characterized by water-conserving features such as thick cuticle and sunken stomatal pits. x-ray diffraction Technique utilized to study atomic structure of crystalline substances by noting the patterns produced by x-rays shot through the crystal.  xylem Tissue in the vascular system of plants that moves water and dissolved nutrients from the roots to the leaves; composed of various cell types including tracheids and vessel elements. Plant tissue type that conducts water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves. Z zebroid A hybrid animal that results from breeding zebras and horses. Z lines Dense areas in myoŞbrils that mark the beginning of the sarcomeres. The actin Şlaments of the sarcomeres are anchored in the Z lines.  zone of differentiation Area in plant roots where recently produced cells develop into different cell types. zone of elongation Area in plant roots where recently produced cells grow and elongate prior to differentiation. zone of intolerance The area outside the geographic range where a population is absent; grades into the zone of physiological stress. zone of physiological stress The area in a population's geographic range where members of population are rare due to physical and biological limiting factors. zygomycetes One of the division of the fungi, characterized by the production of zygospores; includes the bread molds. zygospore In fungi, a structure that forms from the diploid zygote created by the fusion of haploid hyphae of different mating types. After a period of dormancy, the zygospore forms sporangia, where meiosis occurs and spores form. zygote A fertilized egg. A diploid cell resulting from fertilization of an egg by a sperm cell.
__________________
The Me you have always known, the Me that's a stranger still. |
| The Following 6 Users Say Thank You to Last Island For This Useful Post: | ||
ahmed470 (Saturday, November 06, 2010), alifuturcsp (Friday, August 28, 2009), ARSHAD MEHMOOD (Wednesday, August 22, 2007), Mohsin Ehsan LL.M (Friday, August 28, 2009), Sabah Hunzai (Sunday, September 27, 2009), safdarmehmood (Thursday, May 15, 2008) | ||
|
#25
|
|||
|
|||
|
With Due Differences And Refferences I Would Like To Say That It Is An Extreamly Good,hardworking, And Creditable Effort By All The Organisors Of This Forum To Provide More Precise And Comprehensive Notes,guidline,and Written Help To All Your Joniours Without Any Aspiration
I Pray For Your Success In Every Field Of Life Thanks With Regards |
|
#26
|
|||
|
|||
|
first of all i would like to say thank for your(island) very usefull and comprehensive contribution to css forum your all posts are very use full specially for beginners. Second the most important is i want to appear i css2010 examination i wnt to give css exams but some of domestic problems i could not . My qualification is B.A after F.Sc Pre-eng.My main concern is that after fsc i am totally out of field i gave BA exams just after one week prepration bcoz i am doing job in a private job in a pharmaceuticals. I have not enough knowledge and there is veru short time behind for css 2010.
But one Thing is clear in my mind that i want to give the exams 2010 and insallah want to qualify. So dear brother if you give me some suggestions and guide me in this regard than please guide me in detail that what i should do? and what should be my stratgy to achieve my set target.Please if you have time than kindly guide me Regards |
 |
«
Previous Thread
|
Next Thread
»
|
|
 Similar Threads
Similar Threads
|
||||
| Thread | Thread Starter | Forum | Replies | Last Post |
| WEb Building GLossary Terms | Janeeta | Computer Science | 3 | Monday, November 04, 2019 12:09 AM |
| Glossary of Business terms | Princess Royal | Business Administration | 17 | Monday, February 25, 2008 08:36 PM |
| Glossary Of Islamic Terms | Sureshlasi | Islam | 1 | Thursday, November 29, 2007 02:49 AM |
| Glossary of Poetry Terms | Sureshlasi | English Poetry | 2 | Tuesday, November 13, 2007 12:39 AM |
















