Carbohydrates
The carbohydrates are the compounds which provide energy to living cells. They are compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen with a ratio of two hydrogens for every oxygen atom. The carbohydrates we use as foods have their origin in the photosynthesis of plants. They take the form of sugars, starches, and cellulose.
The name carbohydrate means
"watered carbon" or carbon with attached water molecules. Many carbohydrates have empirical formuli which would imply about equal numbers of carbon and water molecules. For example, the glucose formula
C6H12O6 suggest six carbon atoms and six water molecules.
Signifcance of carbohydrates
Soil carbohydrates
Carbohydrates consitute 5 to 25% of the organic matter in most soils. Plant remains contribute carbohydrates in the form of simple sugars, hemicellulose, and cellulose, but these are more or less decomposed by bacteria, actinomycetes and fungi, which in turn synthesize polysaccharides and other carbohydrates of their own.
The significance of carbohydrates in soil aries largely from the ability of complex polysaccharides to bind inorganic soil particles into stable aggregates. Carbohydrates also form complexes with metal ions, and they serve as building blocks for humus synthesis. Some sugars may stimulate seed germination and root elongation. Other soil properties affected by polysaccharides include cation exchange capacity (attributed to COOH groups of uronic acids) , anion retention (occurence of NH2 groups), and biological activity (energy source for microorganisms).
The major groups of carbohydrates
They can be divided into 3 subclasses:
1. Monosaccharides, which are aldehyde and ketone derivatives of the higher polyhydric alcohols.
2.Oligosaccharides, a large group of polymeric carbohydrates consisting of a relatively few monosaccharide units.
3.Polysaccharides- contain many monomeric units (8 or more)
The carbohydrates material in soil occurs as:
1. free sugars in the soil solution
2. complex polysaccharides
3. polymeric molecules of various sizes and shapes which are so strongly attached to clay and/or humic colloids.
Sugars
The sugars are the carbohydrates which are used directly to supply energy to living organisms. A key group of the sugars have the molecular formula C6H12O6. This group includes glucose, which may exist in either straight-chain or ring forms. Others are fructose, galactose, and mannose. Such sugars are called monosaccharides.
Pairs of ring-form sugars can link to form disaccharides such as common table sugar (sucrose), lactose, and maltose. More complicated linked structures form polysaccharides.
Starches
Starches are carbohydrates in which 300 to 1000 glucose units join together. It is a polysaccharide which plants use to store energy for later use. Starch forms in grains with an insoluble outer layer which remain in the cell where it is formed until the energy is needed. Then it can be broken down into soluble glucose units. Starches are smaller than cellulose units, and can be more readily used for energy. In animals, the equivalent of starches is glycogen, which can be stored in the muscles or in the liver for later use.
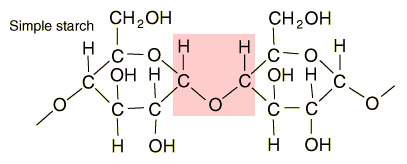
Foods such as potatoes, rice, corn and wheat contain starch granules which are important energy sources for humans. The human digestive process breaks down the starches into glucose units with the aid of enzymes, and those glucose molecules can circulate in the blood stream as an energy source. Tillery, et al. point out an interesting example of this enzyme-catalyzed breakdown process. If you chew on a piece of bread for a while, it will begin to taste sweet because the enzymes in saliva are already beginning to break down the starch into glucose, a sugar.
Cellulose
Cellulose is a form of carbohydrate in which some 1500 glucose rings chain together. It is the chief constituent of cell walls in living organisms. Wood is mostly cellulose, making cellulose the most abundant type of organic compound on the Earth.
Cellulose molecules tend to be straight chains, and the fibers which result from collections of cellulose molecules have the strength to form the supporting structures of plants. Even though human digestion cannot break down cellulose for use as a food, animals such as cattle and termites rely on the energy content of cellulose. They have protozoa and bacteria with the necessary enzymes in their digestive systems. Cellulose in the human diet is needed for fiber.
http://images.google.com/imgres?imgu...PK204%26sa%3DN
http://images.google.com/imgres?imgu...PK204%26sa%3DN